Browser Use vs Axiom: Which Browser Automation Tool Wins in December 2025?

If you're researching this Browser Use vs Axiom comparison, you're probably stuck deciding between learning Python for automation or using a visual tool that records your clicks. Browser Use gives developers flexibility with AI-driven browser control, while Axiom targets people who want to avoid code entirely. The problem is that neither approach is perfect, and your choice depends on your technical background and what you're trying to automate.
TLDR:
- Browser Use requires Python skills while Axiom needs no coding but both break when websites change
- Axiom only runs on Chrome and needs paid plans for cloud execution; Browser Use needs your own servers
- Neither tool handles 2FA or CAPTCHA well, blocking common workflows like invoice downloads
- Skyvern solves these gaps with built-in authentication, cross-site workflows, and auto-scaling cloud execution
What Browser Use Does and How It Works
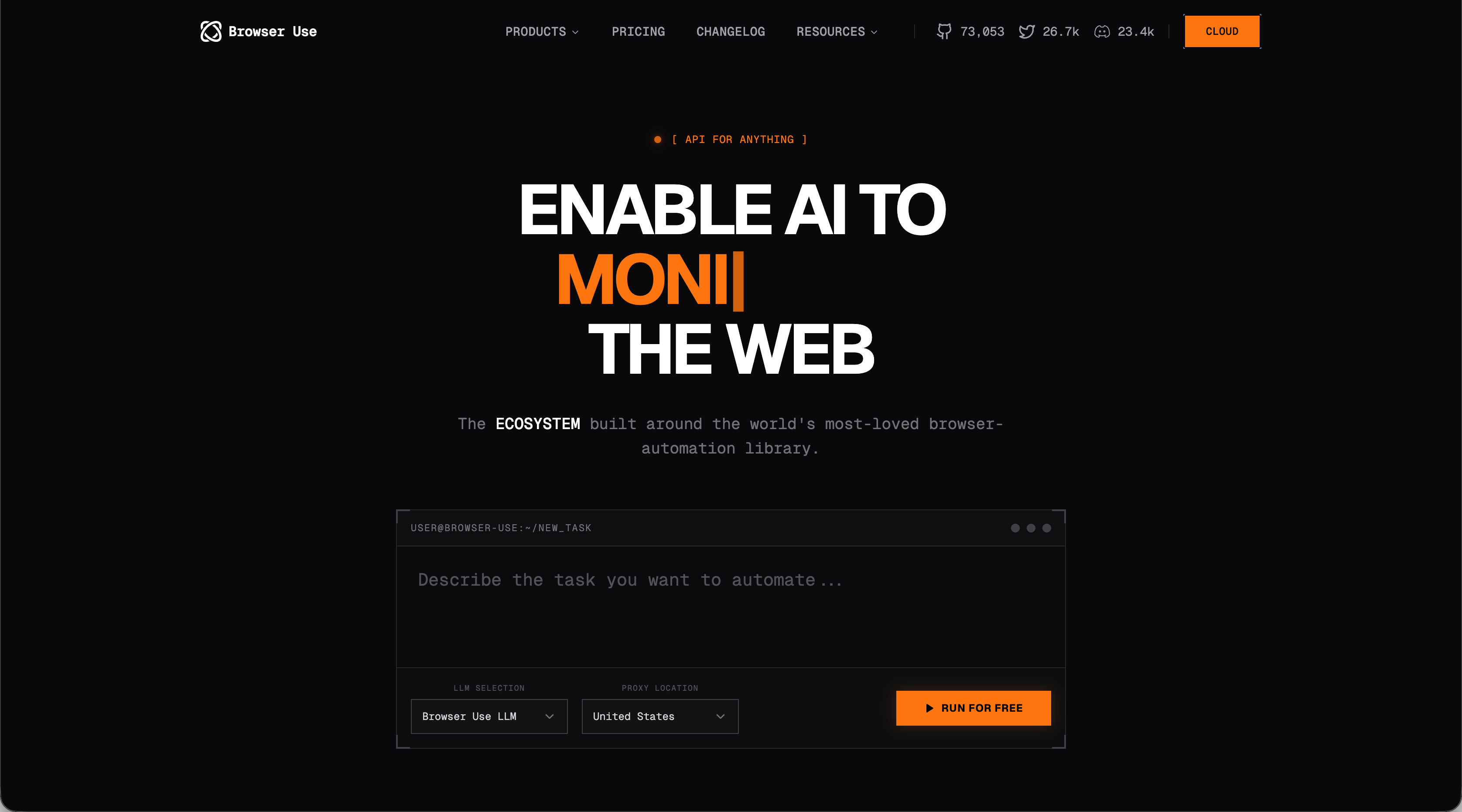
Browser Use is an open-source Python library that empowers AI agents to control web browsers through natural language instructions. Instead of writing explicit code for every click and form field, you describe the task and the library executes it.
The library combines Playwright for browser automation with LLMs for understanding and planning. It requires Python 3.11 or higher and handles task interpretation, execution planning, element navigation, and actions like clicking, form filling, and file downloads.
You can either self-host the library or use their cloud offering, which manages agents, browsers, persistence, authentication, cookies, and LLMs. Browser Use targets developers and technical users comfortable working with Python and managing their own infrastructure.
What Axiom Does and How It Works
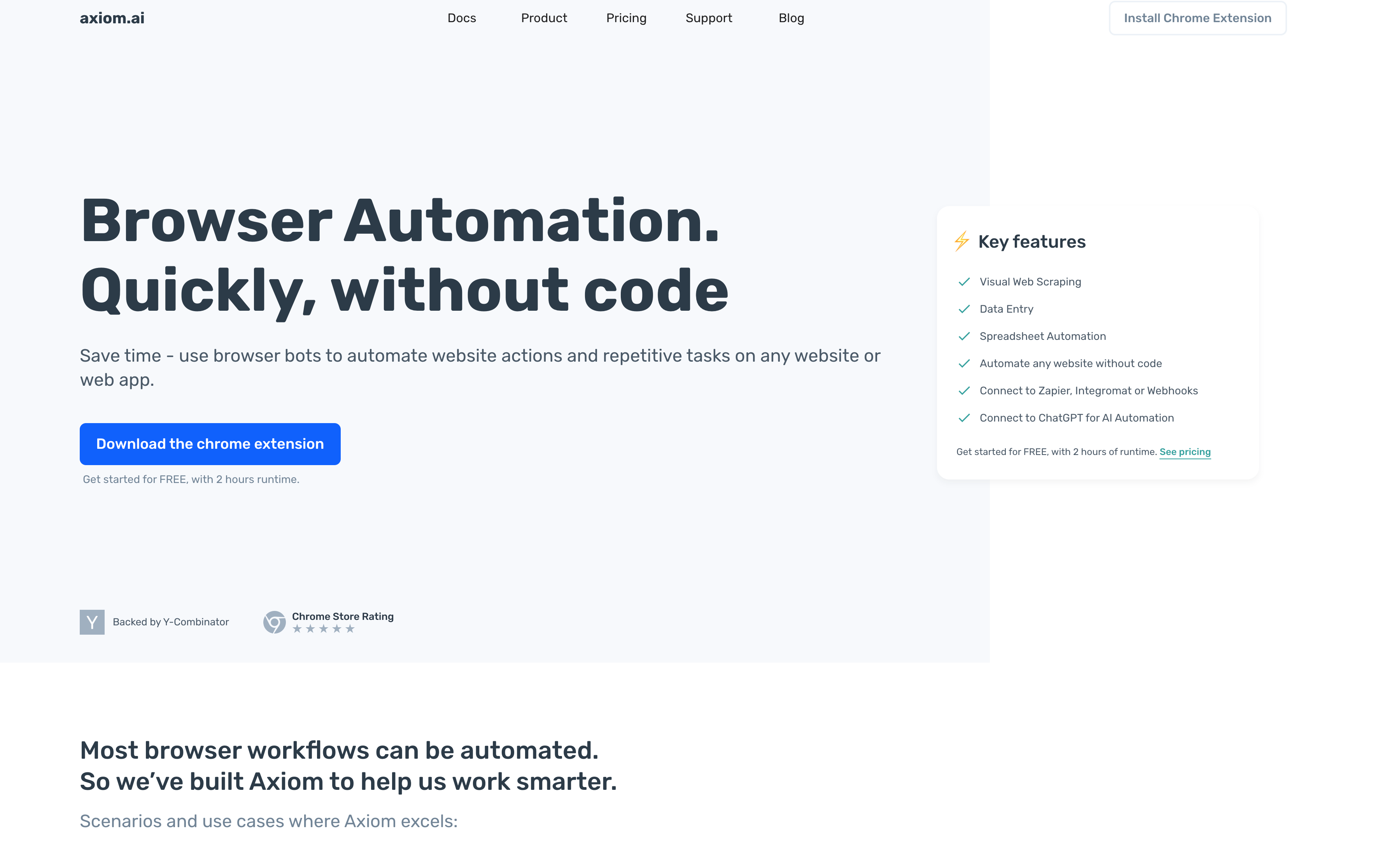
Axiom targets non-technical users who want to automate repetitive browser tasks without writing code. It's a Chrome extension that lets you record clicking and typing actions directly in your browser, then replay them as automated workflows. The tool is built on Puppeteer, a web automation framework, and provides a visual interface for creating bots. You interact with websites normally while Axiom records your actions, turning them into reusable automation sequences.
Unfortunately, Axiom only works on Chrome, so you can't run automations on other browsers. The pricing structure creates limitations: cloud execution requires a paid plan, while the free tier only supports local automation. Free users must keep their browser open and running for automations to work, which isn't practical for tasks that need to run independently or on schedules.
Technical Requirements and Setup Complexity
When comparing these two browser automation tools, it's important to look at the technical requirements and how difficult it will be to get setup and started.
- Browser Use requires programming skills from day one. You'll configure Python environments, manage dependencies, and write code to define automation tasks. Teams without Python developers will need to hire or train staff before getting started.
- Axiom eliminates coding but adds different complexity. The visual interface lets you build automation through clicks and recordings instead of code. You still need to understand automation logic, when to add conditions, how element selectors work, and how to structure multi-step sequences.
The Bottom Line
Your background determines the learning curve. Developers comfortable with Python can launch Browser Use quickly, though they'll need to learn effective prompt structuring for AI agents. Non-technical users can install Axiom in minutes, but mastering workflow logic and troubleshooting failures requires practice.
When it comes down to it, neither tool offers true plug-and-play simplicity. Browser Use demands technical skills upfront. Axiom swaps coding for visual configuration, which sounds simpler but often causes confusion when recordings fail to replay or when you need to modify existing automations.
Browser Compatibility and Cross-Platform Support
Obviously, browser compatibility should be a key decision-making factor for a browser automation tool. So how do these two solutions tackle cross-platform support?
- Browser Use supports Chromium-based browsers through Playwright, including Chrome, Edge, and other Chromium variants. This matters when teams use different browsers or workflows require testing across multiple environments.
- Axiom only works with Chrome. If different departments use different browsers, you can't standardize automation across your organization. Every workflow, user, and machine must run Chrome.
The Bottom Line
Teams working across macOS, Windows, and Linux can run Chrome, but Axiom can't use Safari on Mac or work in environments where Chrome isn't available or approved. Browser Use handles these scenarios through Playwright's cross-platform support. The browser constraint also limits testing capabilities. You can't verify how automations behave in different browsers, which matters for form filling or data extraction from sites that render differently.
Handling Dynamic Websites and Maintenance Requirements
Many browser automation tools choke on dynamic websites. They rely on analyzing DOM or other structural elements so when the design changes, the automation breaks. So how does this affect Browser Use and Axiom?
- Website changes break Axiom automations regularly. When a site redesigns its layout, updates its CSS classes, or changes element IDs, your recorded workflows stop working. You'll need to re-record affected steps, sometimes rebuilding entire sequences from scratch. The recording model creates brittleness. Axiom captures specific element selectors during recording, and those selectors must remain stable for playback to succeed. Even minor updates can require manual intervention to identify and update broken steps.
- Browser Use handles layout changes better through AI interpretation. The LLM analyzes page structure and content to make decisions, reducing dependence on specific selectors. Large scale redesigns or unusual layouts can still confuse the agent, requiring prompt adjustments or additional guidance.
The Bottom Line
Maintenance burden scales with automation complexity and website volatility. Simple tasks on stable sites need minimal updates. Complex workflows across frequently updated sites require constant monitoring and fixes.
Scalability and Infrastructure Management
Selecting a browser automation tool like Browser Use or Axiom requires you to think about how the tool will scale as your automation needs expand...and the infrastructure requirements to support that. For a broader view of available options, check out our guide to the best intelligent process automation tools. Here's how Browser Use and Axiom tackle scalability and infrastructure:
- Browser Use requires you to provision your own infrastructure. Running concurrent agents means allocating CPU, memory, and browser instances yourself. Scaling to hundreds of agents requires building orchestration systems and managing distributed resources. Self-hosting gives control but adds overhead. You'll handle server provisioning, load balancing, and failure recovery. Teams without DevOps resources face challenges when automation demands spike.
- Axiom's cloud execution removes infrastructure management but caps concurrency by pricing tier. The free plan limits you to one bot at a time. Running more simultaneous bots requires paid tiers, with costs increasing as concurrency grows.
Bottom Line
Browser Use lets you optimize infrastructure costs and scale without concurrency limits, but you manage everything. Axiom simplifies operations but charges for scale.
Authentication and Complex Workflow Handling
Authentication creates serious roadblocks for automation tools. Two-factor authentication, CAPTCHA challenges, and session management require specialized handling that, unfortunately, neither Browser Use nor Axiom handles well. So how do they handle it?
- Browser Use lacks built-in authentication capabilities. Teams must build custom tools for 2FA codes, authenticator app integration, or CAPTCHA solving services. This adds development overhead for workflows behind login walls.
- Axiom records logged-in sessions and stores cookies, but this approach fails when sessions expire or sites trigger re-authentication. The tool cannot solve CAPTCHAs or respond to 2FA prompts during runs. Authentication failures halt the entire workflow.
Multi-step sequences across different websites present another obstacle. Browser Use chains actions through code and passes data between steps. Axiom handles basic sequences but fails when later steps require extracted data from earlier ones or need conditional logic based on authentication status.
The Bottom Line
These gaps prevent full automation of common business workflows. Procurement processes with vendor portals, invoice downloads requiring 2FA, and form submissions with CAPTCHA protection need substantial workarounds to function.
Skyvern as a Complete Automation Solution
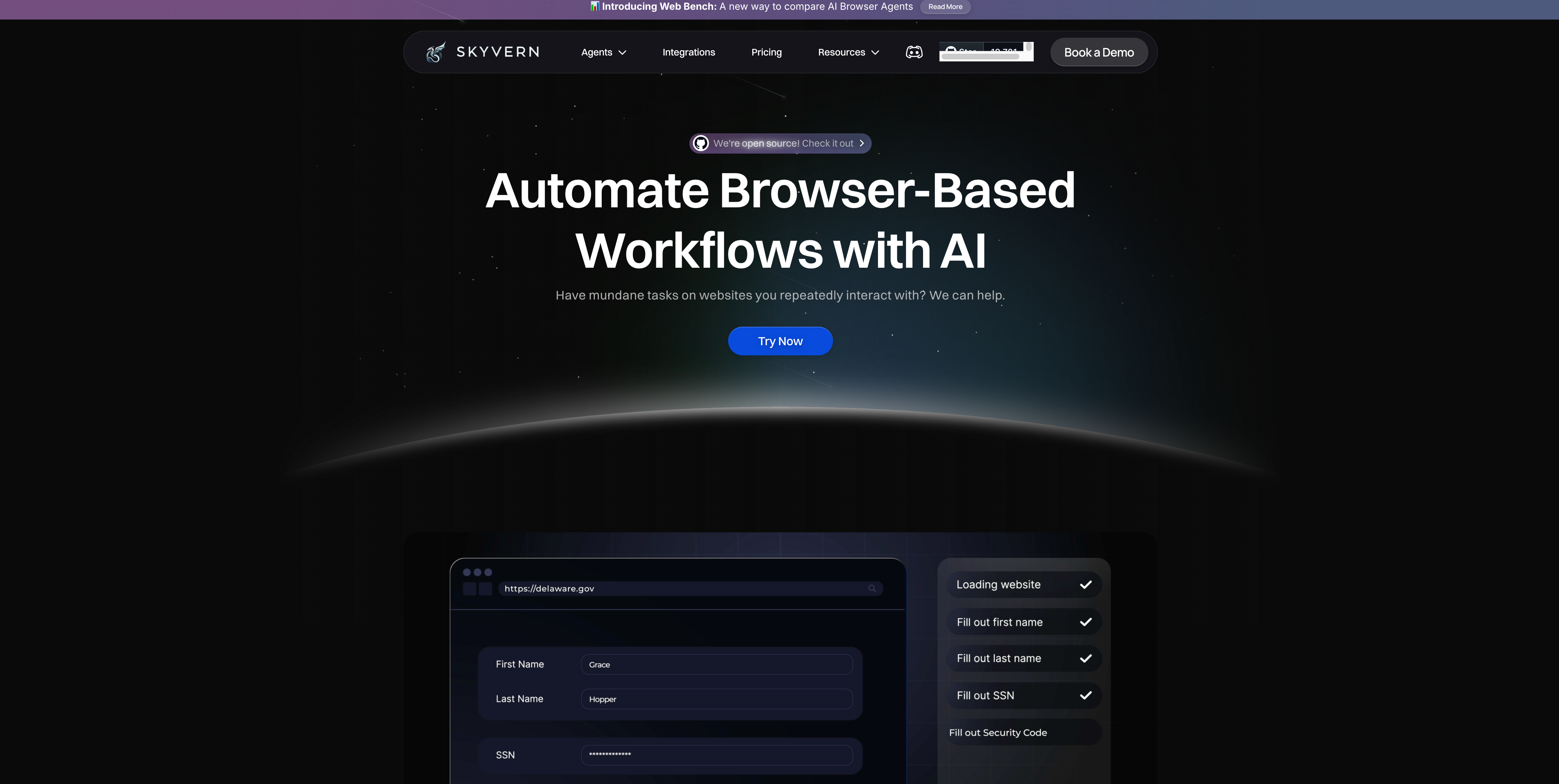
We built Skyvern to solve the core limitations of both approaches. Our LLM and computer vision system interprets page content and structure in real time, which means no brittle selectors breaking workflows or complex Python code to maintain.
Authentication works out of the box. Skyvern handles 2FA, TOTP, and CAPTCHA solving natively through simple API access, so workflows don't stall at login screens or require re-recording after website updates. The same workflow runs across different vendor sites without modification. Procurement teams can hit dozens of supplier portals or finance teams can pull invoices from various vendors using a single automation, whereas Axiom needs separate recordings per site and Browser Use requires site-specific code for each.
Our managed cloud execution handles anti-bot detection and scales automatically, removing the infrastructure requirements that Browser Use creates and the maintenance cycles both tools demand.
Final thoughts on browser automation tool selection
Browser Use requires Python skills and infrastructure management, while Axiom trades coding for Chrome dependency and fragile recordings. The browser automation comparison shows both approaches struggle with authentication and website changes. Your automation needs determine which tradeoffs make sense, but the best solution adapts to layout updates automatically and works across different sites without constant fixes.
FAQ
What's the main difference between Browser Use and Axiom?
Browser Use is a Python library for developers that uses AI to control browsers through code, while Axiom is a Chrome extension for non-technical users that records and replays browser actions without coding.
How do I handle website changes with these automation tools?
Axiom requires re-recording workflows when websites update their layouts or element selectors. Browser Use adapts better through AI interpretation but may still need prompt adjustments for major redesigns.
Can Browser Use or Axiom handle 2FA and CAPTCHA challenges?
Neither tool includes built-in authentication support. Browser Use requires custom development for 2FA and CAPTCHA solving, while Axiom relies on stored cookies that fail when sessions expire or re-authentication triggers.
When should I choose self-hosting over cloud execution?
Self-hosting with Browser Use gives you unlimited concurrency and infrastructure control but requires DevOps resources. Cloud execution with Axiom removes server management but limits concurrent bots by pricing tier.
What technical skills do I need to get started with each tool?
Browser Use requires Python 3.11+ knowledge and experience managing dependencies and environments. Axiom needs no coding but you'll need to understand automation logic, element selectors, and workflow sequencing.

