Best Automated UI Testing Tools and Strategies for Development Teams - November 2025

Testing the same flows manually before every release gets old fast. We've rounded up the best automated ui testing tools that handle cross-browser testing, mobile apps, and layout changes without needing constant updates. Here's what you need to know to pick the right one for your team.
TLDR:
- Automated UI testing runs scripts to validate interfaces across browsers and devices in minutes vs hours
- AI-powered tools like Skyvern adapt to layout changes without breaking, unlike traditional XPath-based tools
- Open source options (Selenium, Cypress, Playwright) remove licensing fees but need more setup time
- Mobile testing requires platform-specific tools: Appium for cross-platform, Espresso for Android, XCUITest for iOS
- Skyvern uses LLMs and computer vision to automate workflows on unseen websites without predefined selectors
Manual Versus Automated Testing
Whatever the kind of test, developers use testing tools that execute predefined test cases to verify that buttons, forms, navigation, and visual elements behave as expected across browsers and devices.
When those tests are done manually, though, the UI testing requires testers to repeatedly perform the same actions, which becomes unsustainable when teams need to carry out multiple tests per day.
Automated UI testing, on the other hand, uses scripts and software to validate user interfaces without human intervention. These tests run in minutes, not hours, and catch regressions before they reach production. The automation testing market is growing as organizations recognize that speed and reliability directly impact revenue.
Types of Automated UI Testing Every Development Team Should Know
There are different kinds of automated UI testing, each method serving a specific purpose:
- Functional testing. This kind of testing verifies that UI elements perform their intended actions. When you click a submit button, does the form actually send? Does the login flow authenticate correctly? These tests validate business logic through the interface and catch broken workflows before users do.
- Visual regression. This testing method compares screenshots across code changes to detect unintended layout shifts, color changes, or rendering issues. A CSS update might accidentally break your mobile navigation, and visual tests catch these problems that functional tests miss.
- Cross-browser. This kind of testing validates application consistency across Chrome, Firefox, Safari, and Edge. Browser inconsistencies still exist in 2025, especially with newer CSS features and JavaScript APIs. Automated cross-browser tests identify compatibility issues without manual checking on multiple machines.
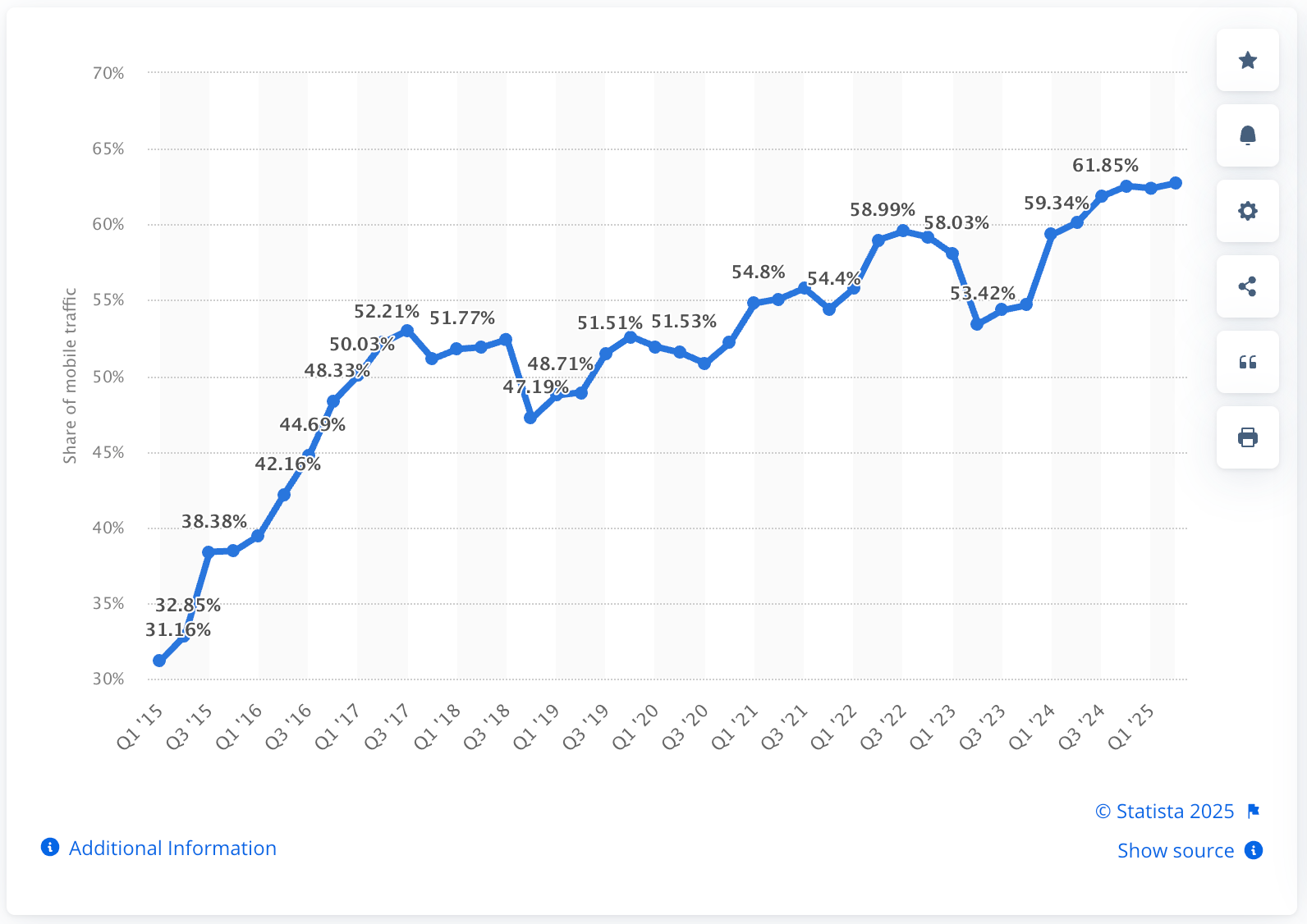
- Mobile UI. This testing validates touch interactions, gestures, screen orientations, and responsive layouts on iOS and Android devices. With mobile traffic representing over half of web usage, mobile-specific testing catches issues like buttons too small for fingers or forms that overflow small screens.
Top 10 Automated UI Testing Tools Comparison
There are lots of tools to carry out one or more of those testing methods. The table below provides a quick overview of the tool, what type it is, what it's best used for, and it's key strength.
Tool | Type | Best For | Key Strength |
|---|---|---|---|
Selenium | Open-source | Cross-browser web testing | Multi-language support, large community |
Cypress | Open-source | JavaScript apps | Fast execution, time-travel debugging |
Playwright | Open-source | Multi-browser automation | Parallel execution, auto-wait capabilities |
Puppeteer | Open-source | Chrome testing | Direct Chrome DevTools integration |
TestComplete | Commercial | Desktop and web | Codeless test creation |
Katalon Studio | Freemium | Teams without coding expertise | Built-in keywords, API testing |
Appium | Open-source | Mobile apps | Cross-platform mobile testing |
Espresso | Open-source | Android apps | Fast, reliable Android UI tests |
XCUITest | Open-source | iOS apps | Native Apple integration |
Skyvern | Open-source/Cloud | AI-driven workflows | Works on unseen sites, adapts to layout changes |
Selenium remains widely adopted due to language flexibility and browser coverage. Cypress gained traction for JavaScript-heavy applications with its developer-friendly approach, while tools like Browser Use offer alternative approaches to browser automation. Skyvern, though, uses LLMs and computer vision to handle websites without predefined selectors, making it resistant to layout changes that break traditional tools.
Open Source Versus Commercial Automated UI Testing Tools
There are always tradeoffs when considering open-source versus commercial offerings.
For instance, open source options like Selenium and Cypress remove licensing fees and offer complete code visibility. You can modify test frameworks to match your requirements, connect with any CI/CD pipeline, and access community forums for troubleshooting. Teams with development experience can extend functionality and resolve issues without waiting on vendors.
That tradeoff, though, is longer setup time and ongoing maintenance. Open source tools need more upfront configuration, and you have to handle problems without dedicated support. Documentation quality varies across projects, and adding capabilities like visual regression testing or cloud-based browser grids requires integrating additional tools.
Commercial solutions, on the other hand, include support contracts, ready-made integrations, and interfaces that shorten implementation timelines. TestComplete and Katalon Studio provide codeless test builders that let QA analysts without programming backgrounds create automated tests.
When it comes down to it, we recommend that you pick open source when you have engineers available to configure and maintain the stack, require specific customizations, or want to avoid vendor dependencies. On the other hand, you should pick a commercial offering when delivery speed outweighs budget constraints, your team lacks automation experience, or you need guaranteed SLAs and compliance certifications.
AI-Powered Automated UI Testing Tools and Benefits
AI-powered testing tools adapt to UI changes without manual script updates. Self-healing capabilities use computer vision and LLMs to identify elements even when developers modify class names, IDs, or page structure. Traditional tests break when a button moves or gets renamed, while AI-driven tools locate elements by visual context and semantic meaning instead of brittle XPath selectors.
Intelligent test generation analyzes application behavior to suggest test cases that maximize coverage with minimal redundancy. These tools identify user paths that lack test coverage and automatically create scripts that validate critical workflows. 55% of organizations now use AI tools for development and testing, with adoption reaching 70% among mature DevOps teams.
The big gain here is that AI reduces maintenance overhead by automatically updating tests when interfaces change. For example, when Skyvern encounters a website it has never seen, it uses LLMs to understand form fields, navigation patterns, and workflow logic without predefined selectors. This eliminates the constant script maintenance that consumes QA team capacity.
Visual validation benefits from AI through semantic understanding which is better than trying to achieve pixel-perfect matching. Tools distinguish intentional design changes from actual bugs, ignoring acceptable variations like dynamic content or timestamps while flagging layout breaks and rendering errors.
Mobile Automated UI Testing Tools and Frameworks
Testing mobile UI can be challenging simply because of the modality: mobile apps are on specific operating systems on specific devices. Thankfully, there are a number of different tools that you can use to automate these test
- Appium supports cross-platform mobile testing with a single test suite that runs on both iOS and Android. The framework handles native apps, hybrid apps, and mobile web applications through WebDriver protocol. Teams with shared codebases avoid maintaining separate test suites for each operating system, though the abstraction layer can slow execution compared to native alternatives.
- Espresso syncs automatically with Android's UI thread, running tests directly on the device without HTTP requests between test code and app. The framework uses view matchers for element identification and action methods for user interaction simulation. Android-only teams get faster feedback during development than cross-platform tools provide.
- XCUITest runs at the system level with full access to iOS accessibility features through Apple's native testing framework in Xcode. Tests written in Swift or Objective-C integrate directly with Apple's development ecosystem. iOS-focused teams see better performance than cross-platform options, though tests require Apple hardware.
- Detox handles React Native applications with automatic synchronization for network requests, animations, and timers. Flutter apps use the flutter_test package and integration_test framework for widget and integration testing. Framework-specific solutions understand rendering engines better than generic mobile testing tools.
Automated UI Testing Framework Implementation Best Practices
Regardless of what tool you land on, you'll need to build some testing frameworks to make sure your automation is optimized.
We recommend that you first start with a test strategy before selecting tools. That strategy should include an identification of your highest-risk workflows and pages that change frequently, then a prioritization of test cases by business impact instead of coverage percentages. Testing checkout flows and authentication matters more than validating footer links. Finally, you should define clear success metrics like deployment confidence and regression detection rate instead of arbitrary coverage targets.
Once you have that strategy, you need to pair it with a framework that matches your team's skills and application architecture. For example, React applications benefit from frameworks with component testing support like Cypress or Playwright. Teams without coding experience gain more from low-code options like Katalon Studio. Finally, evaluate maintenance overhead alongside capabilities because brittle tests that constantly break waste more time than they save.
Building Sustainable Test Architecture
With your strategy in hand and a framework selected, there are some clear best practices to building a sustainable test architecture.
- First, implement page object patterns that separate UI element locators from test logic. When developers change button IDs or restructure navigation, you update locators in one place instead of editing hundreds of test files. Use data-driven testing to run identical workflows with different inputs, reducing duplicate test code.
- Second, design tests to run independently without relying on execution order or shared state. Parallel execution cuts feedback time from hours to minutes, but only works when tests don't interfere with each other. Create isolated test data for each run instead of depending on specific database states.
- Finally, train teams through pairing sessions where experienced automation engineers work directly with QA analysts and developers. Documentation alone doesn't build competency. Rotate responsibility for maintaining test suites so knowledge spreads beyond a single person who becomes a bottleneck.
Common Challenges in Automated UI Testing and Solutions
Even with those best practices in mind, a good strategy, and a framework that matches your team's skill sets, there are a host of challenges in automating UI testing:
- Test maintenance. This challenge can consume a lot of team time as developers update scripts to match interface changes. Fragile locators break when class names or IDs shift, creating constant rework. Self-healing selectors through AI-powered tools or semantic locators that find elements by role and label instead of implementation details reduce this burden. Page object patterns centralize locator updates to single files instead of scattered test code.
- Test reliability. Flaky tests that pass and fail unpredictably destroy confidence in automation. Race conditions, timing issues, and environment inconsistencies cause intermittent failures. Explicit waits for dynamic content, retry logic for network-dependent operations, and isolated test data prevent state conflicts between parallel runs.
- Element identification. This can fail repeatedly when applications use dynamic IDs or lack stable attributes and is a major challenge in UI testing automation. Accessibility attributes like ARIA labels that rarely change, or computer vision approaches that locate elements by visual context instead of DOM properties, solve this problem.
Cost Analysis and ROI of Automated UI Testing Tools
While open source tools remove licensing fees, they demand engineering hours for setup, configuration, and maintenance. That's why your framework and tool selection needs to factor in infrastructure expenses like cloud-based browser grids, parallel execution environments, and storage for test artifacts. Conversely, commercial tools charge per user or test execution, with enterprise pricing reaching thousands monthly, but they cut implementation time and include support.
An easy way to calculate ROI is to compare manual testing hours saved against automation investment. If your team spends 40 hours per sprint on regression testing and automation reduces that to 5 hours, you save 35 hours of labor each sprint. Multiply saved hours by average hourly cost, then subtract tool licensing and maintenance expenses to find net benefit.
But beware of the hidden costs. These can include training team members, maintaining test suites as applications evolve, and debugging flaky tests. AI-powered tools reduce maintenance overhead by adapting to layout changes without manual script updates, improving long-term ROI despite higher upfront costs compared to basic open source options.
Automated UI Testing Integration with CI/CD Pipelines
The nirvana is to bake your automated UI testing into your CI/CD pipelines. This optimizes the entire testing approach while providing support through DevOps teams.
To do this, you'll need to trigger test execution at strategic points in your delivery pipeline, not running full suites on every commit. Run critical path tests on each pull request, extended regression suites nightly, and comprehensive cross-browser tests before production releases.
Next, configure pipelines to fail builds when tests detect regressions, preventing broken code from advancing. Set different thresholds for test types: block deployments on functional test failures but warn on visual differences that need human review. Teams using AI-powered test automation report 40% faster release cycles through intelligent failure classification.
Then, you should integrate reporting dashboards which show trends across builds instead of single test runs. Track failure rates, execution times, and flaky test patterns to identify maintenance needs before they impact velocity.
Finally, handle failures through automatic retries for known flaky tests while immediately alerting teams to new failures. Route notifications to appropriate channels based on failure type: send authentication issues to backend teams and layout breaks to frontend developers.
FAQ
What is the main difference between open source and commercial automated UI testing tools?
Open source tools like Selenium and Cypress eliminate licensing costs and provide full code control, but require more setup time and technical expertise to maintain. Commercial tools include support contracts, ready-made integrations, and codeless interfaces that reduce implementation time but come with recurring subscription fees.
How do AI-powered testing tools reduce maintenance overhead?
AI-powered tools use computer vision and LLMs to identify UI elements by visual context and semantic meaning instead of brittle XPath selectors, automatically adapting when developers modify class names, IDs, or page layouts without requiring manual script updates.
When should I run automated UI tests in my CI/CD pipeline?
Run critical path tests on each pull request to catch immediate issues, execute extended regression suites nightly to validate broader functionality, and perform full cross-browser tests before production releases to balance speed with coverage.
Why do automated tests become flaky and how can I fix them?
Tests fail unpredictably due to race conditions, timing issues with dynamic content, and environment inconsistencies between test runs. Fix flaky tests by implementing explicit waits for asynchronous operations, adding retry logic for network-dependent actions, and isolating test data to prevent state conflicts during parallel execution.
Can automated UI testing tools work on mobile applications?
Yes, tools like Appium support cross-platform testing for both iOS and Android with a single test suite, while native frameworks like Espresso (Android) and XCUITest (iOS) provide faster execution and deeper integration with platform-specific features at the cost of maintaining separate test suites.
Final thoughts on UI testing automation strategies
The tools matter less than how you use them. Automated UI testing with AI removes a lot of the maintenance burden that made older approaches frustrating. Start small with tests that protect your most important features and build confidence before expanding. You'll move faster when your tests actually help instead of just breaking.

